Body cells require oxygen for living. While this molecule is essential for the survival of the cells, on the other hand, in certain circumstances, it can become harmful and give rise to free radicals.
FREE RADICALS
Free radicals are molecules or ions that contain one or more unpaired electrons and which are capable of independent existence. Free radicals are produced in most body cells (mitochondria) as a byproduct of certain metabolic reactions. They are considered responsible for most of the degenerative diseases of aging, and perhaps even cancer (mutations).
Many factors can trigger the generation of free radicals:
- ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS: pollution, active and passive smoking, ultraviolet radiation, prolonged physical and psychological stress, alcohol;
- FACTORS RELATED TO SUBJECT: electron transport in the mitochondria, fatty acid metabolism, the reactions of cytochrome p450, systems reconditioning of phagocytic cells.
Among the most important free radicals that are found in aerobic cells, such as human ones, there are the superoxide (O2–), hydrogen peroxide, also known as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and singlet oxygen.
All cell structures can be damaged by interaction with oxidizing species:
- PHOSPHOLIPID: alteration of membrane fluidity;
- NUCLEIC ACIDS: appearance of break points in the DNA double helix with increased risk of mutations;
- PROTEIN: metabolic (enzymes) and structural.
ENDOGENOUS ANTIOXIDANTS
The body has developed numerous mechanisms to protect themselves from the harmful effects of free radicals, for example, there are some enzymes that can break down and seize oxidizing agents.
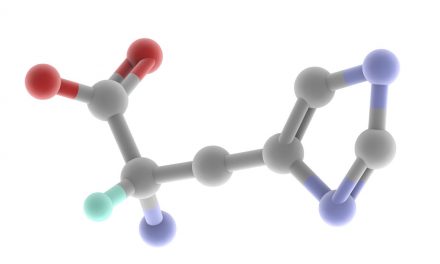
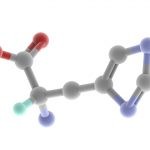
Among these endogenous antioxidants remember superoxide dismutase, catalase, and the most effective antioxidant, glutathione (whose integration occurs via one of the amino acid precursors, the N- acetyl cysteine).
Glutathione incorporates selenium, an antioxidant exogenous that appears to decrease the risk of cancer. The cell also has available additional mechanisms of defense in case the function of endogenous antioxidants is not sufficient .
In recent years there has been much talk of the melatonin antioxidant that according to some studies more than five times the activity glutathione “scavenger “.
EXOGENOUS ANTIOXIDANTS
Some substances present in foods and some dietary supplements are able to positively intervene in the processes of detoxification, activating biological systems shelter. These natural antioxidants are vitamins A, C, E, selenium, carotenoids, lycopene, Q-10 coenzyme and lipoic acid.
ANTIOXIDANTS AND SPORTS
During aerobic exercise, the oxygen consumption of the organism can increase up to 20 times and in skeletal muscle up to 100 times. While this mechanism allows to increase the amount of energy produced, on the other hand dangerously also increases the production of oxidizing agents. In general, oxidative stress is increased muscle by exercise and acute decreased from training.
Sport also improves the disposal mechanisms by enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidants. This feature explains why exercise face look more beautiful and young people who practice it regularly.