Vitamin B7 (Biotin)
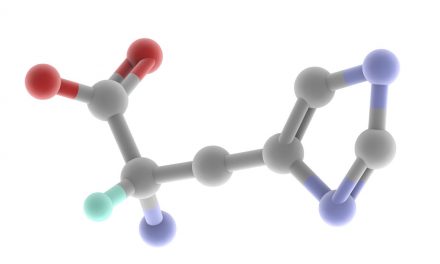
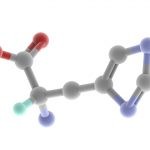
Biotin, also known as vitamin H or coenzyme R, is a water-soluble B-vitamin. Biotin is an important component of enzymes in the body that break down certain substances like fats, carbohydrates, and others. Biotin is necessary for cell growth, the production of fatty acids, and the metabolism of fats and amino acids. Biotin assists in various metabolic reactions involving the transfer of carbon dioxide. It may also be helpful in maintaining a steady blood sugar level. Biotin is often recommended as a dietary supplement for strengthening hair and nails, though scientific data supporting this outcome are weak. Biotin travels in the bloodstream and excess or unused quantities are eliminated in urine. This means the body does not build up reserves of this vitamin, you have to ingest it daily.
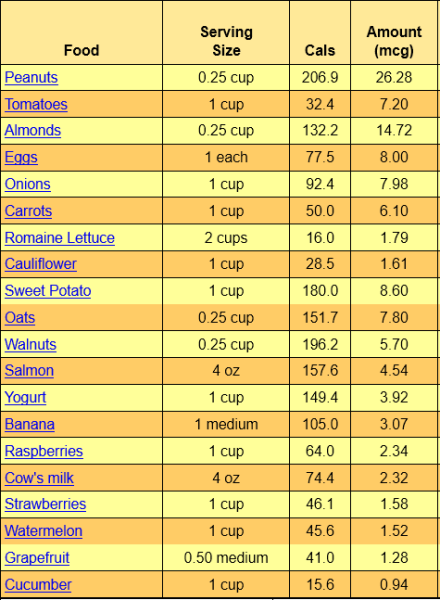
Dietary Sources of Vitamin B7
A wide range of foods contains vitamin B7. None of them have markedly enormous amounts, as is the case with some other vitamins. The following foods have slightly higher amounts:
- Egg yolk (raw). Egg white reduces egg yolk’s biotin effectiveness in the body. People who consume just egg white for many years without biotin supplementation have a slight risk of not getting enough vitamin B7.
- Liver
- Peanuts
- Yeast
- Bread, whole-wheat
- Cheese, cheddar
- Liver
- Pork
- Salmon
- Avocado
- Raspberries
- Cauliflower (raw)
Dietary Deficiency of Vitamin B7
Although biotin deficiency is rare, it can develop during pregnancy or in people who have poor nutrition or experience rapid weight loss. Symptoms of biotin deficiency include hair loss, dry skin, a scaly rash around the eyes or mouth, dry eyes, fatigue, and depression.
Other uses
If Vitamin B7 is important for you because you want skin elasticity and reduce wrinkles, then you must need some products with Verisol® collagen. Furthermore, if your goal is to reduce signs of cellulite then you can use the same product because it also contains Bioactive Collagen Peptides®.