Metabolism is the set of biochemical processes and energy that take place in our bodies, and these reactions are designed to extract and process the energy contained in food, and then direct it to the satisfaction of energy requirements and structural cells. A fine adjustment mechanism provides to balance all these metabolic reactions , depending on the actual availability of nutrients and demands phones.
The existence of living organisms therefore depends on the introduction of a quantity of energy and matter sufficient to meet the metabolic needs, commonly referred to as nutritional needs. In turn, these demands are closely related to the daily energy expenditure: the more calories are burned and many more calories should be introduced. We arrive at this point to give a simple definition and alternative metabolism:
Metabolism is the rate at which our body burns calories to meet his basic needs by this definition, we have that to accelerate our metabolism we simply increase the vital needs of our body, increasing energy expenditure.
Basal Metabolism
It is the minimum amount of energy required by the body for the performance of vegetative functions well over 24 hours, in conditions of complete mental and physical rest, at room temperature (64.4–75.2° F) and strict fasting for 12 hours.
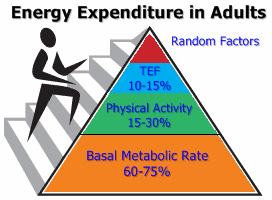
The daily caloric requirement depends on three different components :
- The Basal Metabolic Rate (MB O MBR)
- TEF: Thermic effect of food (also called dynamic action of food)
- Physical Activity
The basal metabolic rate responsible for almost 70% of the daily energy expenditure is influenced by many factors. We list the fundamental ones:
- Power supply: in the fasting metabolism also slows down by 20%.
- Breast-feeding: the mother’s basal metabolic rate increases by about 3-6 %.
- Physical Activity: your metabolic rate remains high even after physical activity.
- Climate: Summer is the best time to lose weight, because when the mercury exceeds 86° F, the metabolism increases slightly. Even temperatures too rigid slow to the same effect.
- Body composition: the muscle tissue is a very metabolically more active than fat. Each kilogram of muscle mass gained raises the body’s metabolism by about 1,5%.
- Body size: the basal metabolic rate, expressed in absolute terms, increases with increasing body surface area. For this reason, tall and slim people have a faster metabolism than individuals of equal weight but shorter people.
- Age: Metabolism is highest in childhood, remains high until early adulthood and begins to decrease after age 30. Between 60 and 90 years fell by around 8% per decade.
- Genetics: we must however, admit it, some people are born with a slow metabolism, others with a faster metabolism.
- Pregnancy: the basal metabolic rate remains stable in the first quarter, rising about 8% to 5 months and 14-22% in the last two months of gestation.
- Hormone levels: many hormones involved in the regulation of body metabolism. The most active in this regard are those produced by the thyroid. Excessive production of these hormones (hyperthyroidism) can even double the basal metabolic rate, while a deficiency (hypothyroidism, goiter) can slow it down considerably. Even the adrenaline is secreted from the adrenal medulla in response to stress psychophysical important, slightly raises the metabolic activity. The growth hormone and testosterone, increasing protein synthesis, may raise in an important way the basal metabolism.
- Gender: through increased muscle mass, basal metabolic rate in humans is higher, by about 7%, compared to the woman. Castration lowers it by 20-25%.
- Lifestyle: sedentary people have a slower metabolism than active during sleep are witnessing a decrease in metabolic rate between 6 and 13% .
- Body temperature: in febrile states the basal metabolic rate increases by about 13% for each degree of temperature above 98.6 °F.
To be continued..